Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will reach 3.8 billion people by 2099. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context. Africa has a large quantity of natural resources and food resources, including diamonds, sugar, salt, gold, iron, cobalt, uranium, copper, bauxite, silver, petroleum, natural gas, cocoa beans, and.
Africa straddles the equator and the prime meridian. It is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate to the southern temperate zones. The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere, with a substantial portion and a number of countries in the Southern Hemisphere. Most of the continent lies in the tropics, except for a large part of Western Sahara, Algeria, Libya and Egypt, the northern tip of Mauritania, and the entire territories of Morocco, Ceuta, Melilla, and Tunisia, which in turn are located above the tropic of Cancer, in the northern temperate zone. In the other extreme of the continent, southern Namibia, southern Botswana, great parts of South Africa, the entire territories of Lesotho and Eswatini and the southern tips of Mozambique and Madagascar are located below the tropic of Capricorn, in the southern temperate zone.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa also is heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies, the historical process is largely a communal one, with eyewitness accounts, hearsay, reminiscences, and occasionally visions, dreams, and hallucinations, crafted into oral traditions, leading some to term them oral civilisations. Time is sometimes mythical and social, and truth generally viewed as relativist. The lack of comprehensive written records has meant that African history was largely written by outsiders, Europeans and Arabs, with contemporary historians tasked with decolonising African historiography. (Full article...)
Selected article –

The history of Maputo, the capital of Mozambique, traces its origins back over 500 years, when a fishing village developed by Maputo Bay on the site where the modern city of Maputo now stands. The first Europeans to discover the bay were Portuguese navigators led by António de Campo in 1502. In 1544, the Portuguese merchant and explorer Lourenço Marques reached the bay and named it Delagoa Bay. The Portuguese established a fort on the site, but were soon forced to abandon it. In 1721, the Dutch East India Company established Fort Lydsaamheid on the bay, but abandoned it due to conflicts with local Africans and the unhealthy environment. In the mid-18th century, the Portuguese returned to the bay, selling ivory to British ships carrying Indian textiles. In 1773, William Bolts of the Trieste Company reached the bay and claimed it for the Holy Roman Empire. Bolts and the Austrians were forced out in 1781 by Portuguese ships sent from Goa.
That year, hoping to prevent other European powers from claiming the area in the future, the Portuguese constructed a fortress on the bay, naming it Lourenço Marques. During the late 18th and early 19th century, the fort was mainly used by French, British, and American whaling ships to stop for provisions. A town grew around the fort starting around 1850, and in 1877, it was elevated to city status. In 1898, the colony of Portuguese Mozambique relocated its capital there. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Lourenço Marques grew both in population and economic development as a port city. Upon Mozambican independence in 1975, the city became the national capital and was renamed Maputo. During the Mozambican Civil War, the city's economy was devastated. When the war ended, the FRELIMO government launched a program to revive the city's economy, and to clean up the city by forcibly removing criminals, squatters, and undocumented residents. Since then, Maputo's economy, centered around its port, has recovered, and stability has returned. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that the pulse stops during the soliloquy of In C Mali?
- ... that South African nurse Stella Madzimbamuto filed an appeal in 1968 with the Privy Council of the United Kingdom that resulted in the Rhodesian government being declared illegal?
- ... that land for a library built for African Americans in Virginia was donated by Pope Pius XII?
- ... that Anderson Stadium in Austin, Texas, is the last high-school football stadium in the state built exclusively for African-American students?
- ... that when the pastor of an African-American church bought the El Dorado, one newspaper wrote that "its occupants are white, and were white"?
- ... that South African anti-apartheid activist Ebrahim Ismail Ebrahim confused warders at the Robben Island maximum security prison by playing Bollywood music?
Categories
Selected biography –
Léopold Sédar Senghor (/sɒŋˈɡɔːr/; French: [sɑ̃ɡɔʁ]; 9 October 1906 – 20 December 2001) was a Senegalese politician, cultural theorist and poet who served as the first president of Senegal from 1960 to 1980.
Ideologically an African socialist, Senghor was one of the major theoreticians of Négritude. He was a proponent of African culture, black identity, and African empowerment within the framework of French-African ties. He advocated for the extension of full civil and political rights for France's African territories while arguing that French Africans would be better off within a federal French structure than as independent nation-states. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
||
| |||
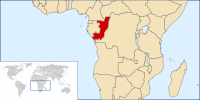
The Republic of the Congo (French: République du Congo; Kongo: Repubilika ya Kongo; Lingala: Republiki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, is a former French colony of western-central Africa. Upon independence in 1960, the former French region of Middle Congo became the Republic of the Congo. A quarter century of Marxism was abandoned in 1990 and a democratically elected government installed in 1992. A brief civil war in 1997 restored former Marxist President Denis Sassou Nguesso.
The Republic of the Congo borders the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south and east, Gabon to the west, Cameroon and the Central African Republic to the north, and Cabinda (Angola) and the Gulf of Guinea to the southwest. The southwest of the country is a coastal plain for which the primary drainage is the Kouilou-Niari River; the interior consists of a central plateau between two basins to the south and north. The capital, Brazzaville, is located on the Congo River, in the south of the country, immediately across from Kinshasa, the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. (Read more...)
Selected city –
Harare (/həˈrɑːreɪ/ hə-RAR-ay), formerly Salisbury, is the capital and largest city of Zimbabwe. The city proper has an area of 982.3 km2 (379.3 sq mi), a population of 1,849,600 as of the 2022 census and an estimated 2,487,209 people in its metropolitan province. The city is situated in north-eastern Zimbabwe in the country's Mashonaland region. Harare is a metropolitan province which also incorporates the municipalities of Chitungwiza and Epworth. The city sits on a plateau at an elevation of 1,483 metres (4,865 feet) above sea level, and its climate falls into the subtropical highland category.
The city was founded in 1890 by the Pioneer Column, a small military force of the British South Africa Company, and was named Fort Salisbury after the British Prime Minister Lord Salisbury. Company administrators demarcated the city and ran it until Southern Rhodesia achieved responsible government in 1923. Salisbury was thereafter the seat of the Southern Rhodesian (later Rhodesian) government and, between 1953 and 1963, the capital of the Central African Federation. It retained the name Salisbury until 1982 when it was renamed Harare on the second anniversary of Zimbabwe's independence from the United Kingdom. The national parliament moved out of Harare upon completion of the New Parliament of Zimbabwe in Mount Hampden in April 2022. (Full article...)
In the news
- 12 February 2024 –
- Two boats collide on the Congo River near Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo; with the death toll remains unclear. (AP)
- 11 February 2024 – 2023 Africa Cup of Nations
- In association football, hosts Ivory Coast win their third Africa Cup of Nations by defeating Nigeria 2–1 in the final. Sébastien Haller scores the winning goal in the 81st minute. (The Guardian)
- 10 February 2024 – Somali civil war
- Four Emirati soldiers and a Bahraini military officer are killed, while ten other people are injured, when a soldier opens fire at a military base in Mogadishu, Somalia, before being killed in the ensuing shootout. Al-Shabaab claims responsibility. (AP)
- 10 February 2024 –
- A Eurocopter EC130 helicopter crashes near Nipton, California, United States, killing all the six people on board, including Nigerian banker Herbert Wigwe. (CBS News)
- 10 February 2024 – 2023–2024 Senegalese protests
- Violent protests occur in Senegal following an announcement by President Macky Sall that presidential elections have been delayed from February 25 to December 15. (Sky News)
- 9 February 2024 –
- At least 18 people are killed during a collision between a bus and a truck on a road in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo. (AP)
Updated: 16:33, 14 February 2024
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ... that Dutch malacologist Adolph Cornelis van Bruggen is an expert in African land snails?
- ... that a 20‑day study reported by BirdLife International discovered 265 species of birds in Nki National Park?
- ... that Kalulu, an African boy who died in 1877, was modeled in Madame Tussauds and attended Dr. Livingstone's funeral in London?
- ... that Samuel Jackman Prescod became the first person of African descent elected to the Parliament of Barbados?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus